Course Description:
The course covers principles underlying IPv6 Network Design, Internet routing protocols (unicast, multicast and unidirectional) with IPv6, algorithmic issues related to the Internet, IPv6 Migration, measurement and performance, next generation Internet (IPv6, QoS) and applications.
Course Objective:
The main objective of this course is to provide knowledge of different concepts of advanced networking with IPv6 including network design, routing, migration etc.
Course Contents
Unit 1: Introduction to Networking (6 Hrs.)
- 1.1. OSI Model
- 1.2. IPv4 addressing overview
- 1.3. VLSM & CIDR
- 1.4. Operational and managerial issues of Legacy IPv4 networking
- 1.5. Introduction to smart networking
- 1.6. Overview of Programmable networks: SDN and NFV
- 1.7. IPv6 network migration status
Unit 2: IP Next Generation (8 Hrs.)
- 2.1. Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6)
- 2.2. History of IPv6
- 2.3. IPv6 Header Format
- 2.4. Features of IPv6
- 2.5. IPv6 Addressing
- 2.5.1. Unicast addressing and its types
- 2.5.2. Anycast addressing
- 2.5.3. Multicast addressing and its scope
- 2.6. Static and Dynamic addressing with IPv6
- 2.7. IPv6 extension headers
Unit 3: ICMPv6 and Neighbor Discovery (6 Hrs.)
- 3.1. ICMPv6 General Message Format
- 3.2. ICMPv6 Error and Information Message Types
- 3.3. ICMPv6 features and its comparison with ICMPv4
- 3.4. Neighbor Cache and Destination Cache
- 3.5. Neighbor Discovery Processes and Messages
- 3.6. Path MTU Discovery
- 3.7. MLD overview
Unit 4: Security and Quality of Service in IPv6 (4 Hrs.)
- 4.1. Types of Threats
- 4.2. Security Techniques
- 4.3. IPSEC Framework
- 4.4. QoS Paradigms
- 4.5. QoS in IPv6 Protocols
Unit 5: IPv6 Routing (5 Hrs.)
- 5.1. RIPng
- 5.2. OSPF for IPv6
- 5.3. BGP extensions for IPv6
- 5.4. PIM-SM & DVMRP for IPv6
Unit 6: IPv4/IPv6 Transition Mechanisms(8 Hrs.)
- 6.1. Migration Strategies
- 6.2. Tunneling, dual stack and translations
- 6.3. Transition techniques
- 6.3.1. 6RD
- 6.3.2. Dual-stack lite
- 6.3.3. Stateful/Stateless AFT
- 6.3.4. 464XLAT, CGNAT
- 6.3.5. Other recent techniques
Unit 7: Future networking (8 Hrs.)
- 7.1. Operation of SDN and NFV
- 7.2. Introduction to SDN based IPv6 Networking
- 7.3. SDN migration methods and practices
- 7.4. Features of Software-Defined IPv6 Networks (SoDIP6)
- 7.5. SoDIP6 Network Deployment: Challenges and Risks
- 7.6. SoDIP6 based NGN
- 7.7. Routing in Multi-Domain SoDIP6 Networks
Laboratory Works:
For the lab work, one PC to one student either in virtual environment or real environment will be provided. Students will be divided into group of 3 students. The working environment and machine connectivity will look like the following:
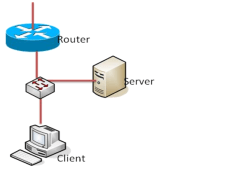
Tools Needed: TCPDUMP & WIRESHARK, VMWare Environment, Linux/FreeBSD, Windows
- Lab 1: Enable IPv6 in Windows/Linux
- Lab 2: IPv6 Header Analysis
- Lab 3: IPv6 Packet analysis (neighbor/router solicitation/discovery)
- Lab 4: Unicast Routing Implementation using Zebra-OSPF & OSPF phase analysis
- Lab 5: Multicast Routing Implementation using XORP-PIM/SM & PIM/SM phase analysis
- Lab 6: SDN enabled IPv6 network implementaion with Mininet
- Lab 7: ONOS, SDN-IP implementation for routing implementaiotn in SoDIP6 network
Reference Books:
- Silvia Hagen: IPv6 Essentials, O’reilly
- Joseph Davies: Understanding IPv6; eastern economy edition
- SDN and NFV simplified: A Visual Guide to Understanding Software Defined Networks and Network Function Virtualization, by Jim Doherty
Prerequisite:
Networking & Communications Fundamentals