2077
Digital Logic
Full Marks: 60
Pass Marks: 24
Time: 3 hours
Attempt any two questions: (2 x 10 = 20)
- Design a combinational circuit that generates 9’s complement of a BCD number.
- Implement the following function using PLA.
- w(A,B,C,D) = ∑(2,12,13)
- x(A,B,C,D) = ∑(7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15)
- y(A,B,C,D) = ∑(0,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,10,11,15)
- z(A,B,C,D) = ∑(1,2,8,12,13)
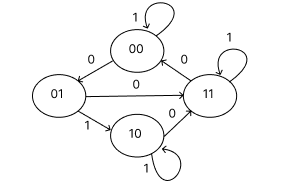
- Design a sequential circuit specified by the following state diagram using T-Flip-Flop.
Attempt any eight questions: (8 x 5 = 40)
- List two major characteristics of digital computer. Represent -6 (negative six) in 8 bits in signed magnitude, signed -1’s complement and signed -2’s complement respectively. Represent decimal number 4673 in a) octal and b) BCD.
- Where is CMOS suitable to use? Define Power dissipation. Show that the positive NAND gate is a negative NOR gate and vice versa.
- This question is unknown. Let us know it you find it.
- Design a full subtractor circuit with three inputs x, y, B_in and two outputs Diff and B_out. The circuit subtracts x-y-B_in where B_in is the input borrow, B_out is the output borrow and Diff is the difference.
- Design a 4-bit even parity generator.
- What is the difference between a serial and parallel transfer? Explain how to convert serial data to parallel and parallel data to serial. What type of register is needed?
- Explain negative edge triggered D flip-flop with necessary logic diagram and truth table.
- Illustrate the use of Binary ripple counter and BCD ripple counter.
- Write short notes on (any two):
- a) RTL
- b) State Reduction
- c) POS